Difference Between Semi-Open and Closed Centrifugal Pumps
July 15, 2025
Top 10 Reasons Why Industrial Pumps Fail (And How to Prevent Them)
August 13, 2025Introduction - Why Centrifugal Pumps Fail
Please review this blog and based on its content, provide the best 3 introduction variations. The introduction should be concise—2 to 3 paragraphs maximum, with each paragraph limited to 3 lines. The total word count for the introduction should be between 100 and 150 words. The language must be simple, humanized, and directly relevant to the blog’s context.
Five critical warning signs consistently predict centrifugal pump failure: unusual vibrations, pressure inconsistencies, temperature rises, seal leakage, and increased power consumption. Each symptom has identifiable causes and proven solutions that prevent expensive emergency repairs. Recognizing these patterns early saves both time and money.
With over 20 years of pump manufacturing experience, Jay Khodiyar Pumps has identified the most critical failure patterns that affect industrial facilities worldwide. Early detection and proper intervention can extend pump life significantly while reducing maintenance costs.
Why Do Centrifugal Pumps Fail?
Understanding the root causes of centrifugal pump failure helps industrial facilities implement better maintenance strategies:
1. Cavitation Damage: Cavitation occurs when vapor bubbles form and collapse within the pump, causing erosion and damage to impeller surfaces. This phenomenon typically results from insufficient NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head) or operating the pump outside its design parameters.
2. Seal and Bearing Failures: Mechanical seals and bearings are wear components that deteriorate over time due to friction, contamination, or inadequate lubrication. These components often fail first in industrial pump systems, especially in harsh operating environments.
3. Corrosion and Erosion: Chemical processes and abrasive fluids gradually wear down pump components, particularly in chemical processing plants worldwide. Material selection and proper coating applications are crucial for preventing premature wear.
4. Improper Installation or Operation: Misalignment, incorrect sizing, or operating pumps outside their design envelope accelerates wear and reduces lifespan. Many pump failures stem from initial installation errors or operational practices that exceed manufacturer specifications.
5. Lack of Preventive Maintenance: Inadequate maintenance schedules, delayed repairs, and ignored warning signs contribute significantly to unexpected pump failures. Regular inspection and maintenance programs can prevent most catastrophic failures.
5 Warning Signs Your Centrifugal Pump is About to Fail (And How to Fix Them)
1. Unusual Noise or Vibration
Excessive noise and vibration are among the earliest indicators of impending centrifugal pump failure. Normal pump operation produces consistent, low-level vibration and operational sounds. When pumps begin producing grinding, squealing, or rattling noises, internal components are likely experiencing stress or damage.
Common Causes:
- Misaligned shaft coupling
- Worn or damaged bearings
- Impeller imbalance or damage
- Loose foundation bolts
- Cavitation within the pump chamber
How to Fix: Start by checking shaft alignment using dial indicators or laser alignment tools. Inspect bearings for excessive play, unusual heat, or lubrication issues. Balance or replace damaged impellers and ensure foundation bolts are properly torqued. If cavitation is suspected, verify NPSH requirements and suction line conditions.
Prevention: Implement vibration monitoring systems that track baseline measurements and alert operators to changes. Regular bearing lubrication schedules and proper installation procedures prevent most noise-related issues.
2. Inconsistent Flow Rate or Pressure
Flow rate and pressure fluctuations indicate internal pump degradation or system issues that compromise performance. Centrifugal pumps should maintain consistent output when operating within their design parameters. Declining performance often signals wear in critical components.
Common Causes:
- Impeller wear or erosion
- Internal recirculation
- Suction line blockages
- Worn wear rings
- Air entrainment in the system
How to Fix: Measure actual flow rates against pump curves to identify performance gaps. Inspect impellers for wear, erosion, or damage that reduces pumping efficiency. Check wear rings for excessive clearances and replace if necessary. Verify suction line integrity and remove any blockages or restrictions.
Prevention: Monitor pump performance curves regularly and establish baseline measurements. Implement filtration systems to prevent debris from entering the pump, and maintain proper suction line design to prevent air entrainment.
3. Frequent Overheating
Pump overheating indicates internal friction, inadequate cooling, or operation outside design parameters. Excessive heat damages seals, bearings, and other temperature-sensitive components, accelerating wear and reducing pump lifespan significantly.
Common Causes:
- Insufficient lubrication
- Bearing deterioration
- Operating at low flow conditions
- Blocked cooling systems
- Mechanical seal problems
How to Fix: Check bearing lubrication levels and condition, replacing degraded lubricant as needed. Verify pump operating points against manufacturer curves to ensure proper flow conditions. Clean cooling systems and ensure adequate ventilation around the pump. Replace worn mechanical seals that allow process fluid to contact bearings.
Prevention: Establish temperature monitoring protocols with alarm systems for early detection. Maintain proper lubrication schedules and ensure pumps operate within recommended flow ranges to minimize heat generation.
4. Excessive Leakage
Seal leakage is normal in small quantities, but increasing leakage indicates deteriorating seals or other issues that require immediate attention. Excessive leakage wastes product, creates safety hazards, and often leads to complete seal failure if ignored.
Common Causes:
- Worn mechanical seals
- Shaft wear or damage
- Improper seal installation
- System pressure fluctuations
- Chemical compatibility issues
How to Fix: Inspect mechanical seals for wear, cracking, or damage and replace complete seal assemblies when necessary. Check shaft condition and repair or replace if worn beyond tolerance. Verify proper seal installation procedures and ensure chemical compatibility between seals and process fluids.
Prevention: Select appropriate seal materials for specific applications and maintain proper seal flush systems. Monitor leakage rates regularly and establish replacement schedules based on operating conditions and seal performance history.
5. Rising Energy Consumption
Increasing power consumption without corresponding increases in output indicates declining pump efficiency. This warning sign often appears gradually, making it easy to overlook without proper monitoring systems in place.
Common Causes:
- Internal wear reducing efficiency
- Operating outside design parameters
- Electrical issues affecting motor performance
- System resistance changes
- Impeller damage or fouling
How to Fix: Analyze power consumption trends against flow and pressure data to identify efficiency losses. Inspect impellers for fouling, damage, or wear that reduces hydraulic efficiency. Check electrical connections and motor condition to ensure proper power delivery.
Prevention: Implement energy monitoring systems that track power consumption patterns. Regular cleaning of impellers and internal components maintains optimal efficiency, while proper system design prevents operation outside recommended parameters.
Preventive Maintenance: The Key to Pump Reliability
Effective preventive maintenance programs significantly extend centrifugal pump lifespan and prevent unexpected failures:
- Regular Inspection Schedules: Weekly visual inspections, monthly vibration monitoring, and quarterly detailed examinations
- Lubrication Management: Proper bearing lubrication with quality oils and greases appropriate for operating conditions
- Alignment Verification: Semi-annual shaft alignment checks using precision instruments to prevent premature wear
- Performance Monitoring: Continuous tracking of flow, pressure, power consumption, and temperature parameters
- Replacement Planning: Proactive replacement of wear components based on condition monitoring rather than reactive repairs

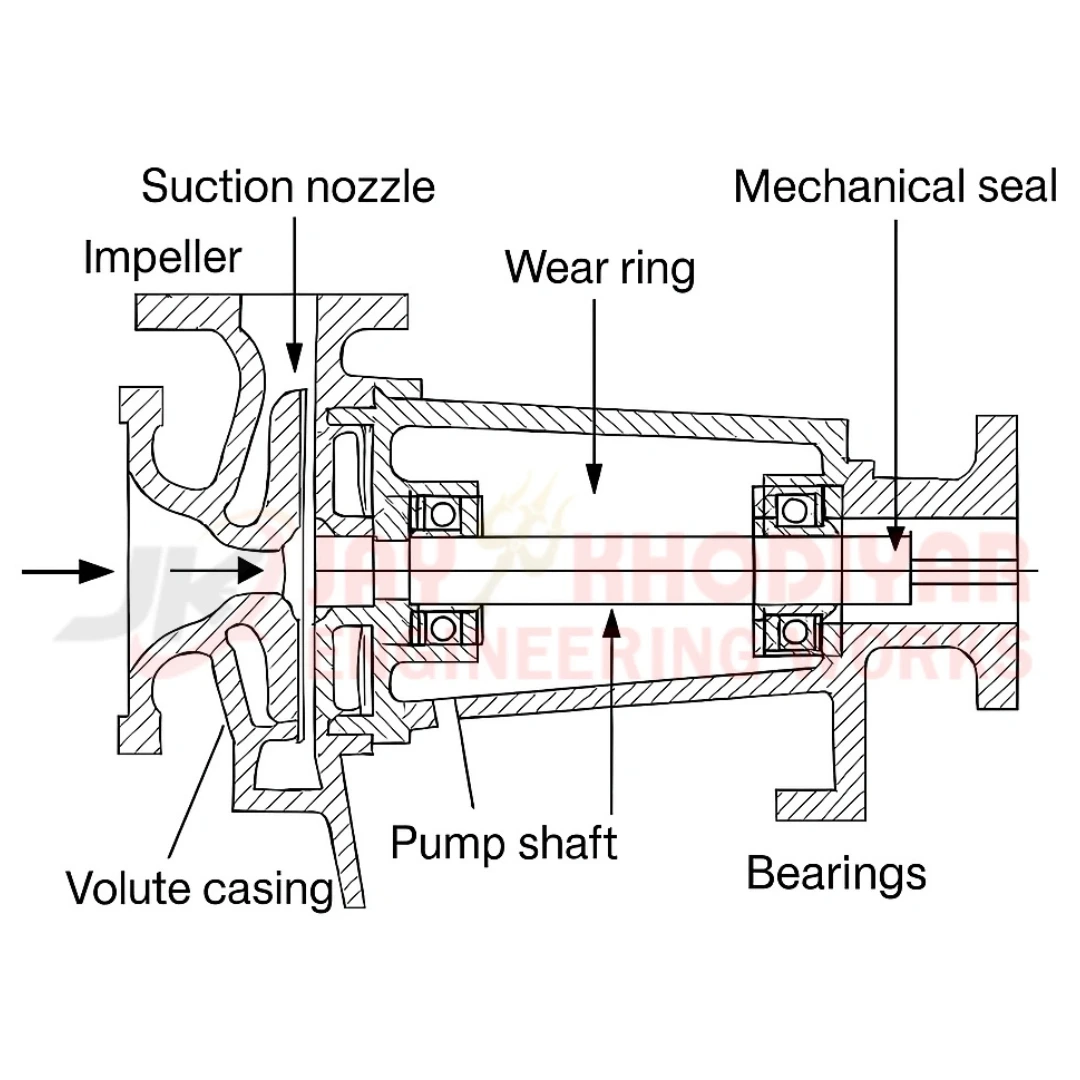
Centrifugal Pump Cross Sectional Drawing
What Are the Major Symptoms of Pump Failure?
Industrial pump failures typically manifest through several key symptoms that maintenance teams can identify:
- Cavitation Sounds: Distinctive crackling or popping noises indicating vapor bubble formation and collapse
- Bearing Temperature Rise: Elevated temperatures in bearing housings signaling lubrication problems or wear
- Seal Leakage Increase: Progressive increase in mechanical seal leakage rates beyond normal limits
- Vibration Amplitude Growth: Gradual or sudden increases in vibration levels indicating internal component problems
- Performance Degradation: Declining flow rates, pressure output, or efficiency measurements over time
- Electrical Anomalies: Abnormal motor current draw, power factor changes, or electrical imbalances
How to Prevent Pump Failures?
Preventing centrifugal pump failures requires a comprehensive approach combining proper design, installation, operation, and maintenance practices. Start with correct pump selection based on actual operating conditions rather than maximum requirements, ensuring adequate NPSH margins and proper materials for the application.
Implement condition-based maintenance programs using vibration analysis, thermal imaging, and performance monitoring to detect problems early. Train operators to recognize warning signs and establish clear protocols for reporting abnormal conditions. Maintain spare parts inventory for critical components and develop relationships with reliable repair services.
Regular maintenance schedules should include lubrication, alignment checks, and performance verification. Document all maintenance activities and use data analysis to identify trends and optimize maintenance intervals. Consider upgrading older pumps with modern monitoring systems that provide real-time condition data and predictive failure warnings.
Why Choose Jay Khodiyar Engineering Works?
Superior pump performance starts with superior manufacturing standards. Jay Khodiyar Pumps combines advanced technology with high-grade raw materials to create industrial pumps that withstand the most challenging operating conditions. Our commitment to quality engineering ensures reliable operation, extended service life, and minimal maintenance requirements across diverse industrial sectors.
Every pump we manufacture meets rigorous quality standards backed by comprehensive testing and validation processes. Our modern facilities utilize cutting-edge machinery and precision manufacturing techniques to deliver pumps that exceed industry benchmarks. With 100% quality assurance and 24/7 technical support, we stand behind every product we deliver.
Contact Jay Khodiyar Pumps today and discover why industries worldwide choose us as their trusted pump partner.